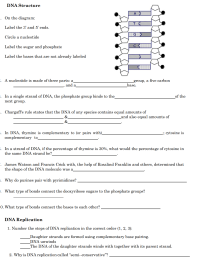
38 nucleotide label
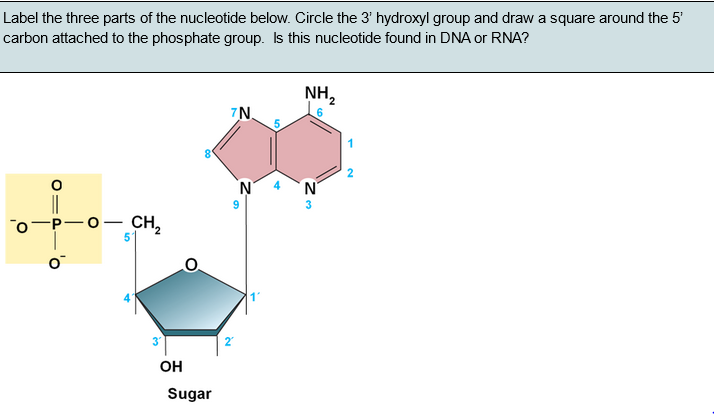
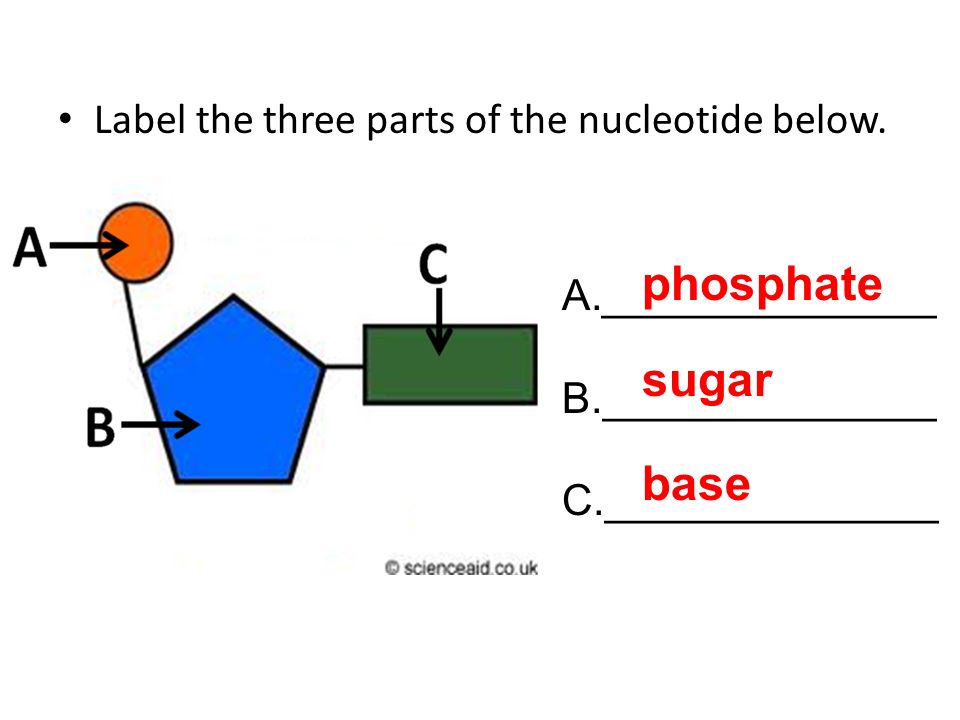
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Nucleotides are the building blocks of the DNA and RNA used as genetic material. Nucleotides also are used for cell signaling and to transport energy throughout cells. You may be asked to name the three parts of a nucleotide and explain how they are connected or bonded to each other. Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA .
What Is a Nucleotide? Definition, Structure, and Function - PrepScholar Each nucleotide is a molecule, so while the bases are extremely important for how the nucleotide is classified and for its eventual function, they cannot form without the other elements that make up the molecule. One of these elements is simple, five-carbohydrate sugars. A nucleotide can contain one of two sugars: Deoxyribose, a monomer of DNA, OR

Nucleotide label
A nucleotide-independent cyclic nitroxide label for monitoring ... by PH Nguyen · 2015 · Cited by 28 — Among spin labels developed, the class of rigid labels have ... a rigid label to nucleic acids in a nucleotide-independent manner has not ... Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA Molecules ... Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these ... Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities.
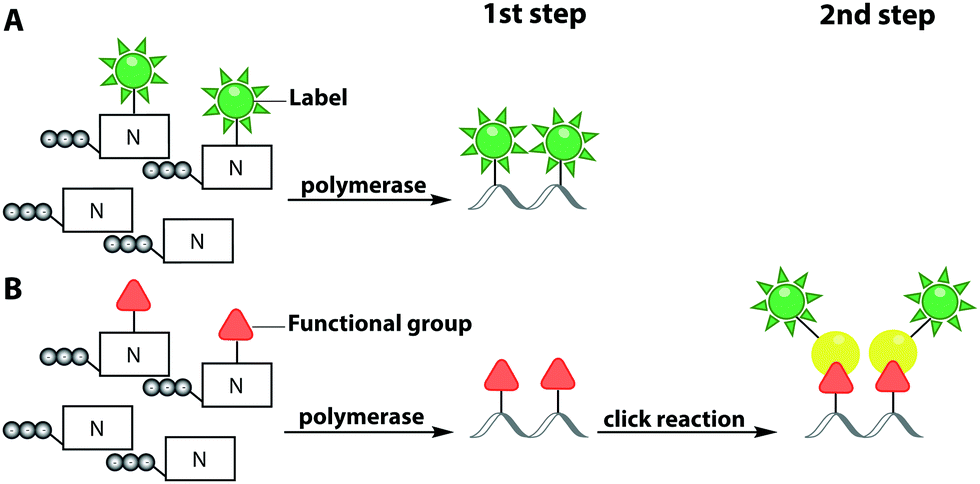
Nucleotide label. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology ... The American Journal of Gastroenterology is pleased to offer two hours of free CME credit with each issue of the Journal.This activity is the result of our reader survey that expressed great interest in journal CME. How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? 19 Jul 2017 — See below The above structure is a color(magenta)"nucleotide". It consists of a: color(orange)"phosphate group" color(red)"5-carbon sugar", ... Fluorescent & Hapten Labeled Nucleotides | PerkinElmer 1 OF 2. Labeled nucleotides are critical elements for sequence detection in a wide variety of techniques including in situ hybridization, microarrays and DNA sequencing. Our fluorescent and hapten labeled nucleotides provide a reliable, sensitive alternative to working with radioactivity through both direct and indirect detection methods. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific This article summarizes enzymatic and chemical methods for labeling nucleic acids. ... T4 RNA ligase, ssDNA, RNA, 3′, modified nucleotide incorporation ...
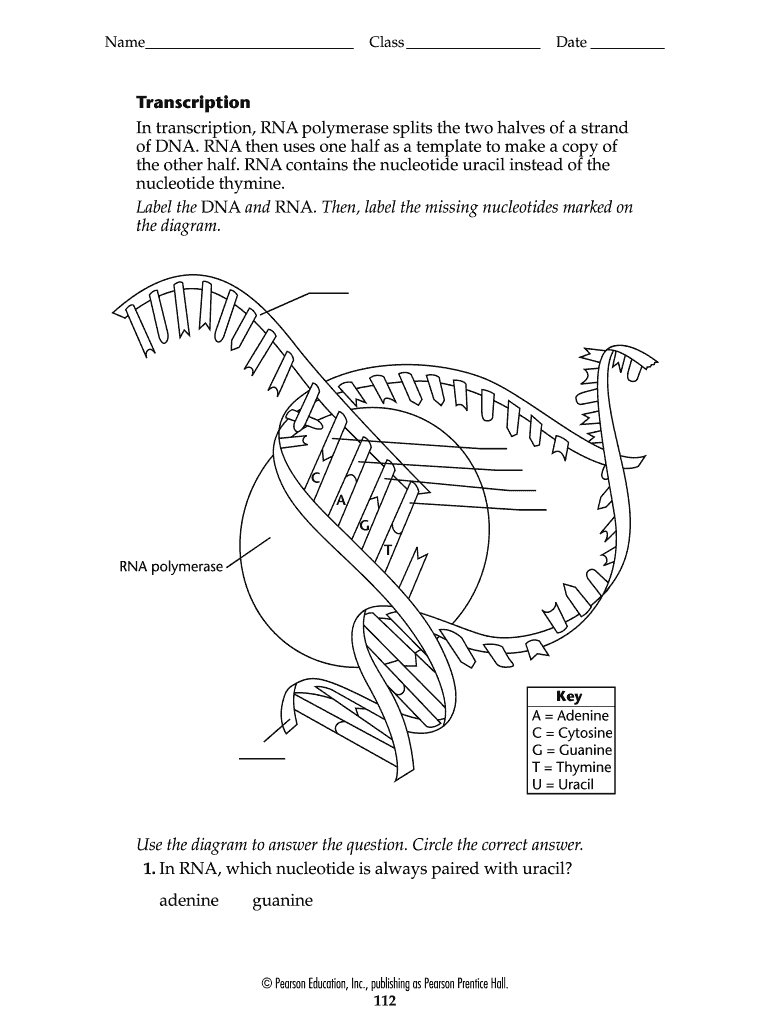
Home - Nucleotide - NCBI The Nucleotide database is a collection of sequences from several sources, including GenBank, RefSeq, TPA and PDB. Genome, gene and transcript sequence data provide the foundation for biomedical research and discovery. Using Nucleotide Quick Start Guide FAQ Help GenBank FTP RefSeq FTP Nucleotide Tools Submit to GenBank LinkOut E-Utilities BLAST The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine. Nucleotide - Wikipedia In experimental biochemistry, nucleotides can be radiolabeled using radionuclides to yield radionucleotides. 5-nucleotides are also used in flavour enhancers as food additive to enhance the umami taste, often in the form of a yeast extract. [3] Contents 1 Structure 2 Synthesis 2.1 Pyrimidine ribonucleotide synthesis Solved The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, | Chegg.com Expert Answer. 100% (23 ratings) Transcribed image text: The diagram depicts the general structure of DNA, with a single nucleotide circled. Label the diagram with the names of the three components of a nucleotide. Answer Bank deoxyribose nitrogenous base phosphate group.
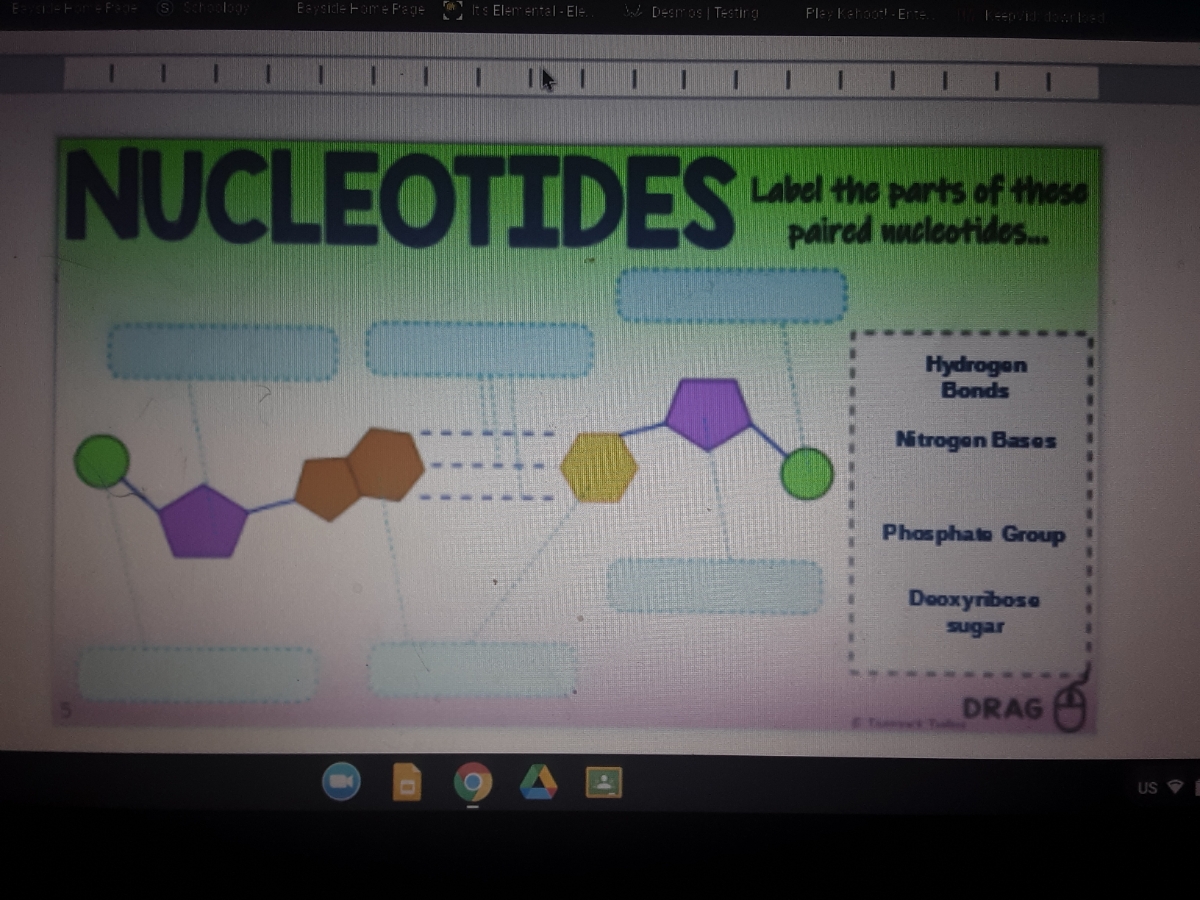
Nucleotide labeled structure Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Nucleotide labeled structure. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. DNA Labeling - NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified ... Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification - A Level Biology Nucleotides are the biological molecules that serve as the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. They are essential for all the functions performed by a living cell. Not only this, but they are also essential for transferring information to new cells or the next generation of the living organisms. Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. - Brainly.com A nucleotide is a molecule composed of a pentose sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. In DNA, there are four types of nucleotides that contain four different classes of nitrogen bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. In RNA, Thymine bases are replaced by Uracil bases.
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and …
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three ... - Toppr The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group; 5-carbon sugar, and; nitrogenous base. solution. expand. Was this answer helpful?
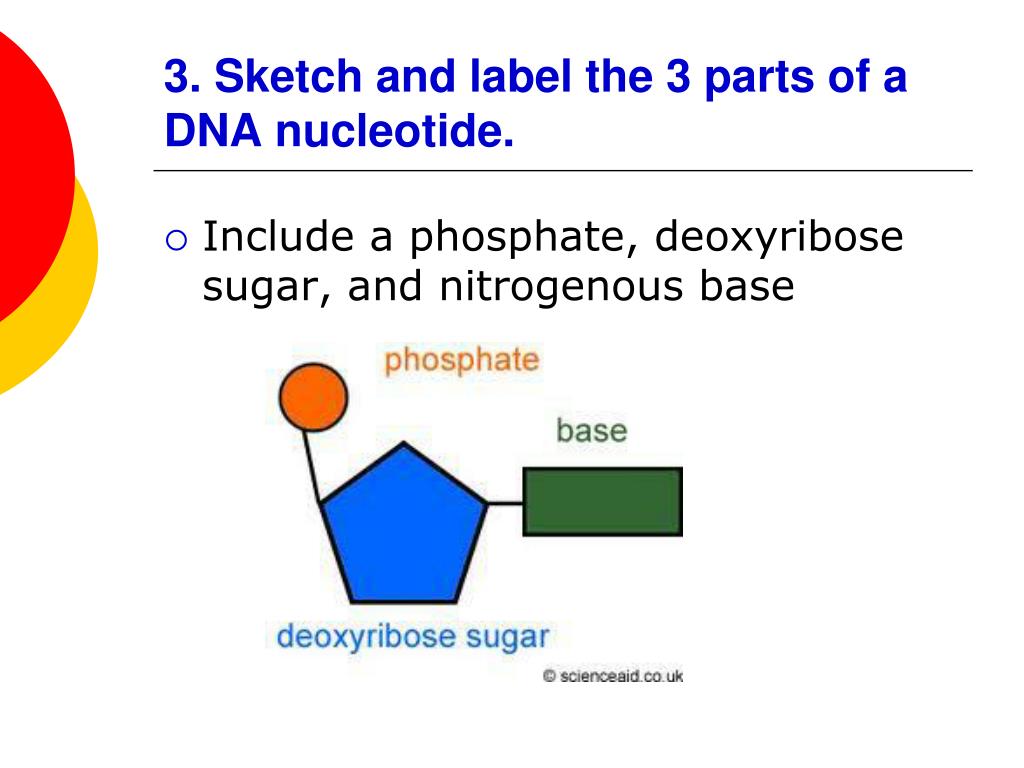
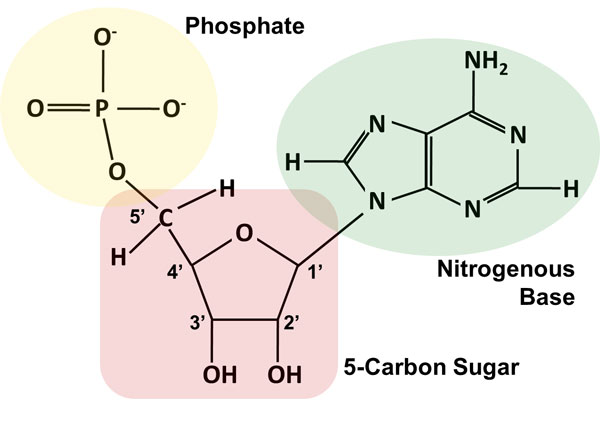
Nucleotides and Bases - Genetics Generation A nucleotide is the basic structural unit and building block for DNA. These building blocks are hooked together to form a chain of DNA. A nucleotide is composed of 3 parts: * five-sided sugar * phosphate group * nitrogenous base (nitrogen containing) Image courtesy of the National Human Genome Research Institution
Primer3 Input (version 0.4.0) Sequence Id: A string to identify your output. Targets: E.g. 50,2 requires primers to surround the 2 bases at positions 50 and 51. Or mark the source sequence with [ and ]: e.g. ...ATCT[CCCC]TCAT.. means that primers must flank the central CCCC.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are molecules which serve as the building blocks, or monomer units, for the creation of important polymers like ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. As mentioned, nucleotides have three component parts: a five-sided carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group.
ENA Browser - European Bioinformatics Institute Customise your own search query and retrieve a set of ENA records tailored to your search criteria. All searches are performed against a subset of the archive specified by the Data type you choose to search against.
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Nucleic acid probes can be labeled with tags or other modifications during synthesis. However, purchasing custom oligonucleotide probes (especially RNA) can be quite expensive depending on the modification and whether costly purification services are required.
Nucleotides in RNA | Science Primer Ribonucleic acids, also called RNA, is the intermediary molecule used by organisms to translate the information in DNA to proteins. RNA is also required for DNA replication, regulates gene expression, and can function as an enzyme. Like DNA, RNA is a polymer - made up of chains of nucleotides.
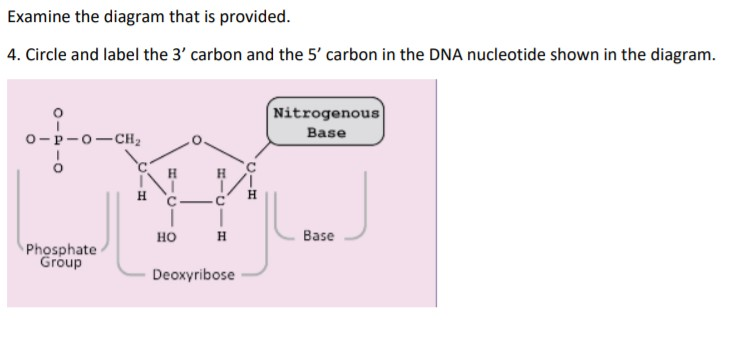
Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar; A phosphate molecule; A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. DNA polymers are strings of nucleotides.
draw a nucleotide and label the three parts - vansyachtcluboutfit Draw a nucleotide and label the three main parts. Which parts are the same in all nucleotides. The three parts of a nucleotide molecule are. Adenine and guanine are purines. Nucleotides Are Added To 3 End Of A Growing Dna Polymer A Draw 2 Nucleotides In A Polymer Draw A Third Nucleotide About To Be Added To The Growing Polymer B Label
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function. DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Fast Track to Gene Annotation and Genome Analysis - DNA Subway DNA Subway Training. DNA Subway Training for Educators; DNA Barcoding and Metabarcoding for CURES Workshops; DNA Barcoding 101. Experimental method and everything else you need to generate DNA barcode sequences to analyze on the DNA Subway Blue Line.
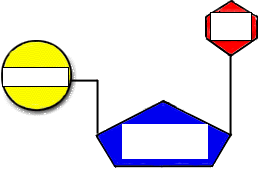
Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A ... Biology College answered Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A Label B Label C Label D Label E Label F Label A is a blue circle, label B is a grey hexagon, label C is adenine, label D is uracil, label E is a pink hexagon, and label F is a blue circle. Advertisement jarahquiroga Answer: A and F are phosphate groups
dna-labeling | NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application.
Genetic Linkage - University of Utah To see how linkage works, let's look at some specific genes. Two of the genes (1 and 2) are relatively far apart (top illustration). Each gene comes in two different versions, or alleles: A and B.
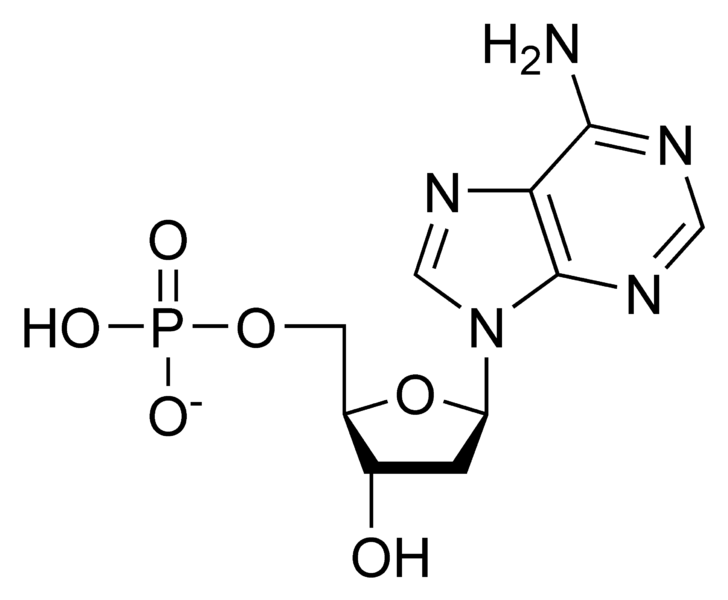
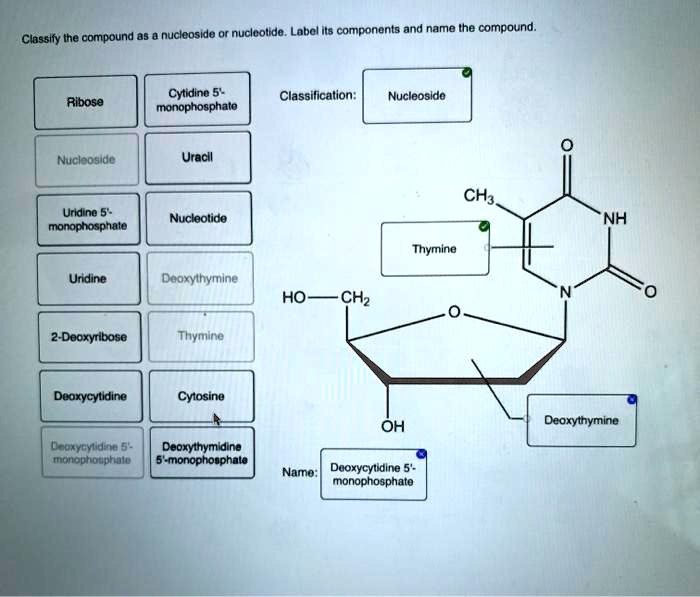
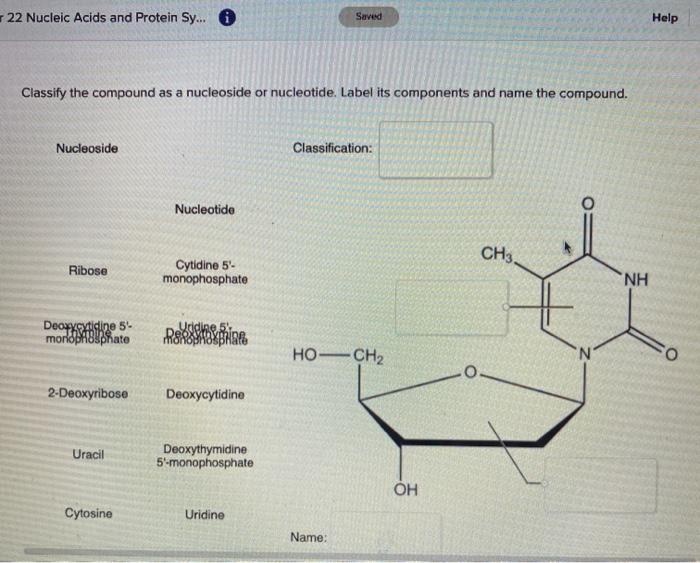
Question : Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide. Label ... Expert Answer. Transcribed image text: Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide. Label its components and name the compound. Nucleoside Classification: Nucleotide NH2 Adbose Adenosine 5- monophosphate 'N 2-Deoxyribose Guanine HO-CH2 N N monophosphate DEuangsing Filme Guanosine Deoxyadenosine 5'-monophosphate Deoxyguanosine 5 ...
Solved Classify the compound as a nucleoside or nucleotide ... - Chegg Label its components and name the compound Adenine Ribo Classification: Nucleoside Deoxydenotine 5 monophosphate Nucleotide Guanine Deoxyguanosine 2.Deoxyribose monophosphate NH Deoxyguanosine Guanosine HOCHE NH Guanine Adenosine Guanonines monophosphate Nucleone ОН Ribose Adenosine monophosphate
DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet Phosphate. Molecule found on the side of a DNA molecule. Double Helix. two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA. Thymine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA. Adenine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide thymine in DNA or with uracil in RNA.
The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona The Structure of DNA. Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of Figure 1 below). The DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral.) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees ...
What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are made up of 3 parts. The first is a distinct nitrogenous base, which is adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. These nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines. Base pairs are formed when adenine forms a hydrogen bond with thymine, or cytosine forms a hydrogen bond with guanine.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
Labeled Nucleotides - Biocompare 2560 products — Labeled nucleotides are available from several suppliers for use in molecular biology. These nucleoside triphosphates, conjugated to moieties ...
Labeled Nucleotides - Biotium Nucleotide analogs and nucleotides labeled with biotin or fluorescent dyes. dCTP and dUTP are available conjugated to our bright and photostable CF® Dyes, ...
BankIt Submission Help: Feature Table File - National Center for ... The first line of the feature table contains the following basic information >Feature Sequence_ID The sequence identifier (Sequence_ID) must match the label used to identify each table's corresponding sequence in the nucleotide FASTA file. Subsequent lines of the table list the features. Prepare the feature table file in a text editor and save it as plain ascii text (not .rtf or …
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities.
Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA Molecules ... Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these ...
A nucleotide-independent cyclic nitroxide label for monitoring ... by PH Nguyen · 2015 · Cited by 28 — Among spin labels developed, the class of rigid labels have ... a rigid label to nucleic acids in a nucleotide-independent manner has not ...














Post a Comment for "38 nucleotide label"